Spring事务
目录
spring事务
声明式事务
声明式事务底层由spring AOP支持
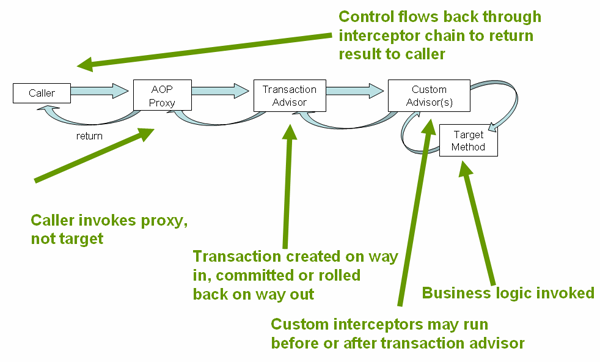
引入依赖spring-boot-starter-jdbc即可使用开箱即用的声明式事务支持
@Service
public class OrderService {
@Autowired
private StoreService storeService;
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void createOrder() {
//create order
//update store
storeService.decreaseStore();
//AOP失效导致事务失效
transactionNotWork();
}
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.DEFAULT, propagation = Propagation.NEVER)
public void transactionNotWork() {
}
}
编程式事务
Using the
TransactionTemplateUsing the
TransactionalOperatorUsing the
TransactionManager
@Service
public class StoreService {
/**
* TransactionDefinition的一种实现
*/
@Autowired
private TransactionTemplate transactionTemplate;
@Autowired
private PlatformTransactionManager txManager;
public Storage findFromMaster() {
return transactionTemplate.execute((status) -> {
//do business
return new Storage(11L);
});
}
public void decreaseStore() {
DefaultTransactionDefinition definition = new DefaultTransactionDefinition();
definition.setIsolationLevel(TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_DEFAULT);
definition.setPropagationBehavior(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW);
TransactionStatus status = txManager.getTransaction(definition);
try {
//do business
} catch (Exception e) {
txManager.rollback(status);
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
txManager.commit(status);
}
public void increaseStore() {
TransactionStatus status = txManager.getTransaction(transactionTemplate);
try {
//do business
} catch (Exception e) {
txManager.rollback(status);
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
txManager.commit(status);
}
public record Storage(Long id) {
}
}
事务失效场景
声明式事务方法内部调用
由于声明式事务底层使用AOP实现,因此失效场景与原因同AOP相同。
事务隔离级别
public enum Isolation {
/**
* Use the default isolation level of the underlying data store.
* <p>All other levels correspond to the JDBC isolation levels.
* @see java.sql.Connection
*/
DEFAULT(TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_DEFAULT),
/**
* A constant indicating that dirty reads, non-repeatable reads, and phantom reads
* can occur.
* <p>This level allows a row changed by one transaction to be read by
* another transaction before any changes in that row have been committed
* (a "dirty read"). If any of the changes are rolled back, the second
* transaction will have retrieved an invalid row.
* @see java.sql.Connection#TRANSACTION_READ_UNCOMMITTED
*/
READ_UNCOMMITTED(TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_READ_UNCOMMITTED),
/**
* A constant indicating that dirty reads are prevented; non-repeatable reads
* and phantom reads can occur.
* <p>This level only prohibits a transaction from reading a row with uncommitted
* changes in it.
* @see java.sql.Connection#TRANSACTION_READ_COMMITTED
*/
READ_COMMITTED(TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED),
/**
* A constant indicating that dirty reads and non-repeatable reads are
* prevented; phantom reads can occur.
* <p>This level prohibits a transaction from reading a row with uncommitted changes
* in it, and it also prohibits the situation where one transaction reads a row,
* a second transaction alters the row, and the first transaction re-reads the row,
* getting different values the second time (a "non-repeatable read").
* @see java.sql.Connection#TRANSACTION_REPEATABLE_READ
*/
REPEATABLE_READ(TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ),
/**
* A constant indicating that dirty reads, non-repeatable reads, and phantom
* reads are prevented.
* <p>This level includes the prohibitions in {@link #ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ}
* and further prohibits the situation where one transaction reads all rows that
* satisfy a {@code WHERE} condition, a second transaction inserts a row
* that satisfies that {@code WHERE} condition, and the first transaction
* re-reads for the same condition, retrieving the additional "phantom" row
* in the second read.
* @see java.sql.Connection#TRANSACTION_SERIALIZABLE
*/
SERIALIZABLE(TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_SERIALIZABLE);
private final int value;
Isolation(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public int value() {
return this.value;
}
}
不同事务隔离级别可能导致的问题
| 隔离级别 | 脏读 | 不可重复读 | 幻读 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 读未提交 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| 读已提交 | ❎ | ✅ | ✅ |
| 可重复读 | ❎ | ❎ | ✅ |
| 串行化 | ❎ | ❎ | ❎ |
事务传播
public enum Propagation {
/**
* Support a current transaction, create a new one if none exists.
* Analogous to EJB transaction attribute of the same name.
* <p>This is the default setting of a transaction annotation.
*/
REQUIRED(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED),
/**
* Support a current transaction, execute non-transactionally if none exists.
* Analogous to EJB transaction attribute of the same name.
* <p>Note: For transaction managers with transaction synchronization,
* {@code SUPPORTS} is slightly different from no transaction at all,
* as it defines a transaction scope that synchronization will apply for.
* As a consequence, the same resources (JDBC Connection, Hibernate Session, etc)
* will be shared for the entire specified scope. Note that this depends on
* the actual synchronization configuration of the transaction manager.
* @see org.springframework.transaction.support.AbstractPlatformTransactionManager#setTransactionSynchronization
*/
SUPPORTS(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS),
/**
* Support a current transaction, throw an exception if none exists.
* Analogous to EJB transaction attribute of the same name.
*/
MANDATORY(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_MANDATORY),
/**
* Create a new transaction, and suspend the current transaction if one exists.
* Analogous to the EJB transaction attribute of the same name.
* <p><b>NOTE:</b> Actual transaction suspension will not work out-of-the-box
* on all transaction managers. This in particular applies to
* {@link org.springframework.transaction.jta.JtaTransactionManager},
* which requires the {@code jakarta.transaction.TransactionManager} to be
* made available to it (which is server-specific in standard Jakarta EE).
* @see org.springframework.transaction.jta.JtaTransactionManager#setTransactionManager
*/
REQUIRES_NEW(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW),
/**
* Execute non-transactionally, suspend the current transaction if one exists.
* Analogous to EJB transaction attribute of the same name.
* <p><b>NOTE:</b> Actual transaction suspension will not work out-of-the-box
* on all transaction managers. This in particular applies to
* {@link org.springframework.transaction.jta.JtaTransactionManager},
* which requires the {@code jakarta.transaction.TransactionManager} to be
* made available to it (which is server-specific in standard Jakarta EE).
* @see org.springframework.transaction.jta.JtaTransactionManager#setTransactionManager
*/
NOT_SUPPORTED(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED),
/**
* Execute non-transactionally, throw an exception if a transaction exists.
* Analogous to EJB transaction attribute of the same name.
*/
NEVER(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NEVER),
/**
* Execute within a nested transaction if a current transaction exists,
* behave like {@code REQUIRED} otherwise. There is no analogous feature in EJB.
* <p>Note: Actual creation of a nested transaction will only work on specific
* transaction managers. Out of the box, this only applies to the JDBC
* DataSourceTransactionManager. Some JTA providers might support nested
* transactions as well.
* @see org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager
*/
NESTED(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NESTED);
private final int value;
Propagation(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public int value() {
return this.value;
}
}
事务传播机制描述的是事务方法调用时事务关联及回滚机制
REQUIRED (默认)
- 支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,则新建事务
- 如果当前存在事务,则加入当前事务,合并成一个事务
REQUIRES_NEW
- 新建事务,如果当前存在事务,则把当前事务挂起
- 这个方法会独立提交事务,不受调用者的事务影响,父级异常,它也是正常提交
NESTED
- mysql不支持嵌套事务,一般是由客户端采用savepoint和rollbackto进行模拟
- 如果当前存在事务,它将会成为父级事务的一个子事务(savepoint),方法结束后并没有提交,只有等父事务结束才提交(由savepoint机制决定)
- 如果当前没有事务,则新建事务
- 如果它异常,父级可以捕获它的异常而不进行回滚,正常提交
- 但如果父级异常,它必然回滚,这就是和
REQUIRES_NEW的区别
SUPPORTS
- 如果当前存在事务,则加入事务
- 如果当前不存在事务,则以非事务方式运行,这个和不写没区别
NOT_SUPPORTED
- 以非事务方式运行
- 如果当前存在事务,则把当前事务挂起
MANDATORY
- 如果当前存在事务,则运行在当前事务中
- 如果当前无事务,则抛出异常,也即父级方法必须有事务
NEVER
- 以非事务方式运行,如果当前存在事务,则抛出异常,即父级方法必须无事务
示例:(以下为伪代码,且两个带有注解的方法不能在同一个类中,否则由于AOP失效会导致事务失效)
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void testMain(){
A(a1);
testB();
throw RuntimeException;
}
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.NESTED)
public void testB(){
B(b1);
B(b2);
}
//a1,b1,b2全部存储失败
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void testMain(){
A(a1);
try{
testB();
}catch(RuntimeException e){
}
A(a2);
}
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.NESTED)
public void testB(){
B(b1);
throw RuntimeException;
B(b2);
}
//a1 a2存储成功,b1 b2存储失败
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void testMain(){
A(a1);
try{
testB();
}catch(Exception e){
}
A(a2);
}
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void testB(){
B(b1);
throw RuntimeException;
B(b2);
}
//a1 a2 b1 b2全部存储失败,由于是同一个事务,即使在外层捕获了异常仍然会回滚
FAQ
如何开启事务?
MySQL 默认是 autocommit=1,也就是说默认是立即提交,如果想开启事务,先设置 autocommit=0,然后用 START TRANSACTION、 COMMIT、 ROLLBACK 来使用具体的事务
查询会不会开启事务?
如果你在 INNODB 事务引擎下,并且 autocommit=1 (默认值), 答案是会
我只是执行单个查询语句,为什么要开事务?
如果你一次执行单条查询语句,则没有必要启用事务支持,数据库默认支持 SQL 执行期间的读一致性; 如果你一次执行多条查询语句,例如统计查询,报表查询,在这种场景下,多条查询 SQL 必须保证整体的读一致性,否则,在前条 SQL 查询之后,后条 SQL 查询之前,数据被其他用户改变,则该次整体的统计查询将会出现读数据不一致的状态,此时,应该启用事务支持
参考资料:
